Unbelievable Tips About How To Explain A Curve Graph Ggplot X Axis

Academic presentation phrases for graphs.
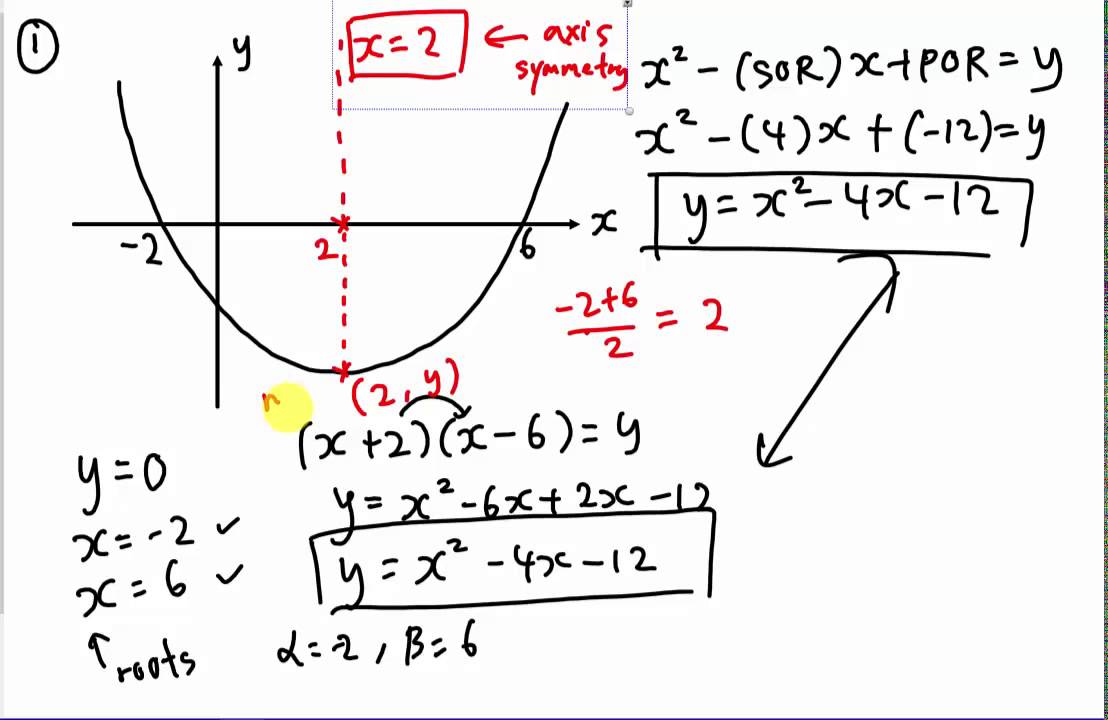
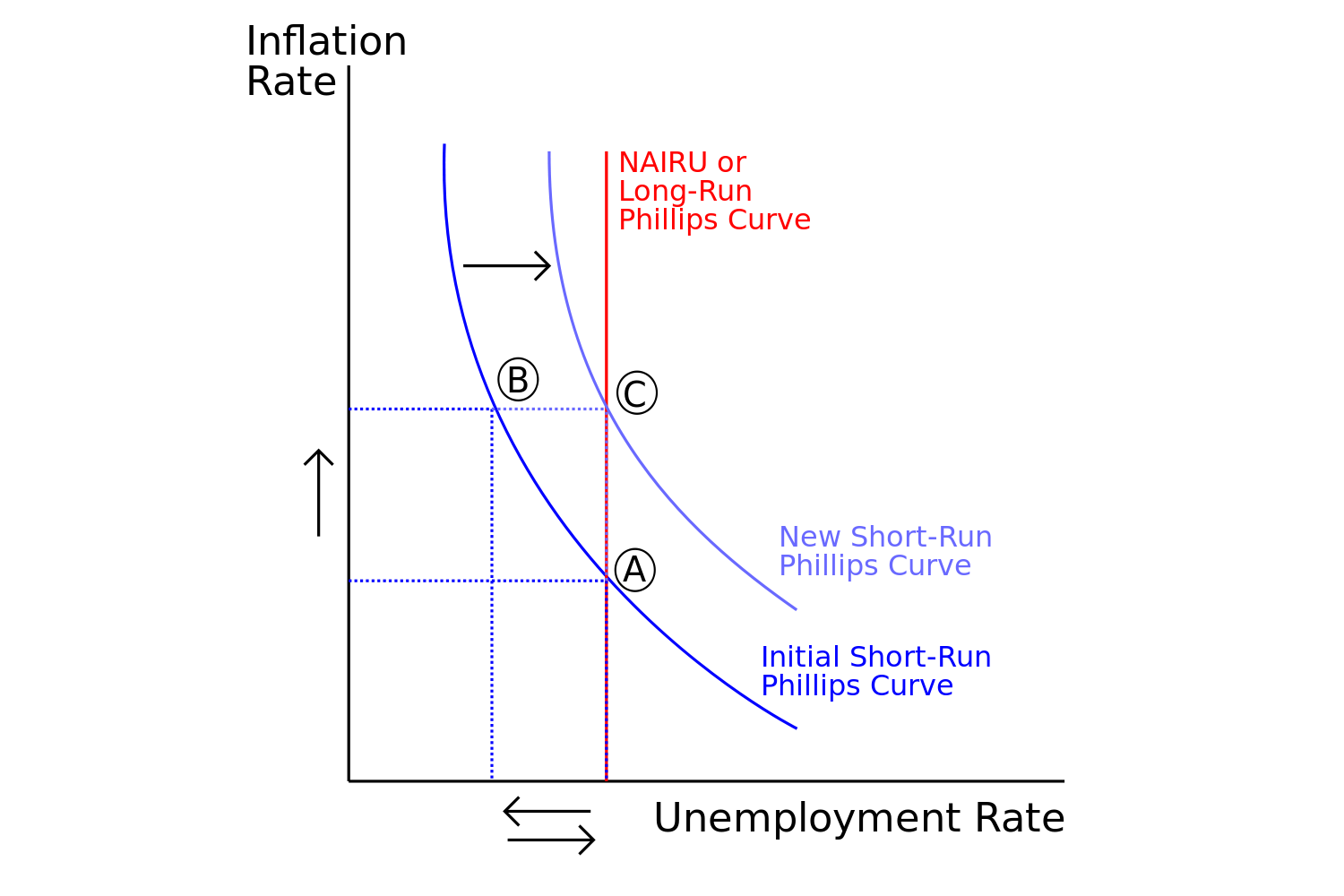
How to explain a curve graph. In this diagram, we have rising demand (d1 to d2) but also a fall in supply. A demand curve is a graph that shows the relationship between the price of a good or service and the quantity demanded within a specified time frame. Part of biology working scientifically.
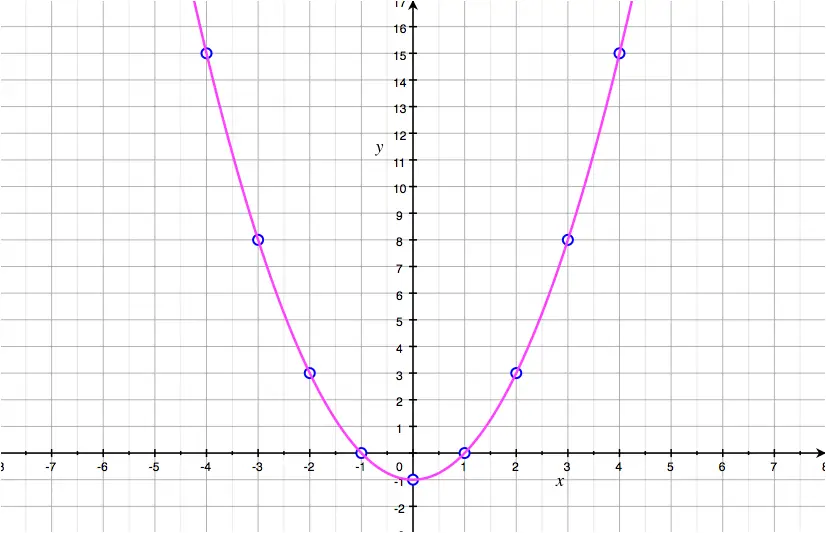
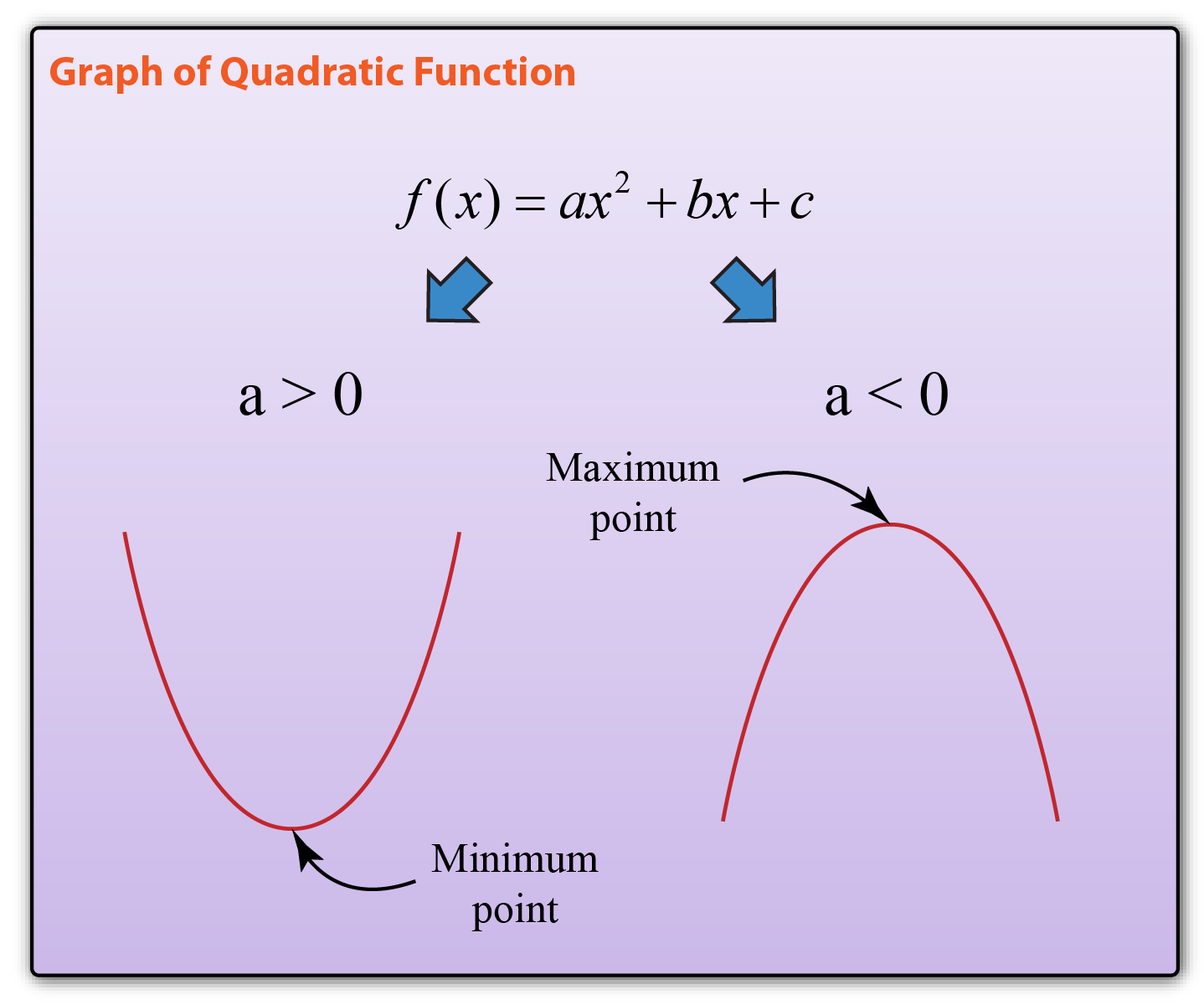
The effect is to cause a large rise in price. Diagram showing increase in price. A curve in mathematics is a line or a shape that is smoothly traced in a plane and has a bent or arc in it.
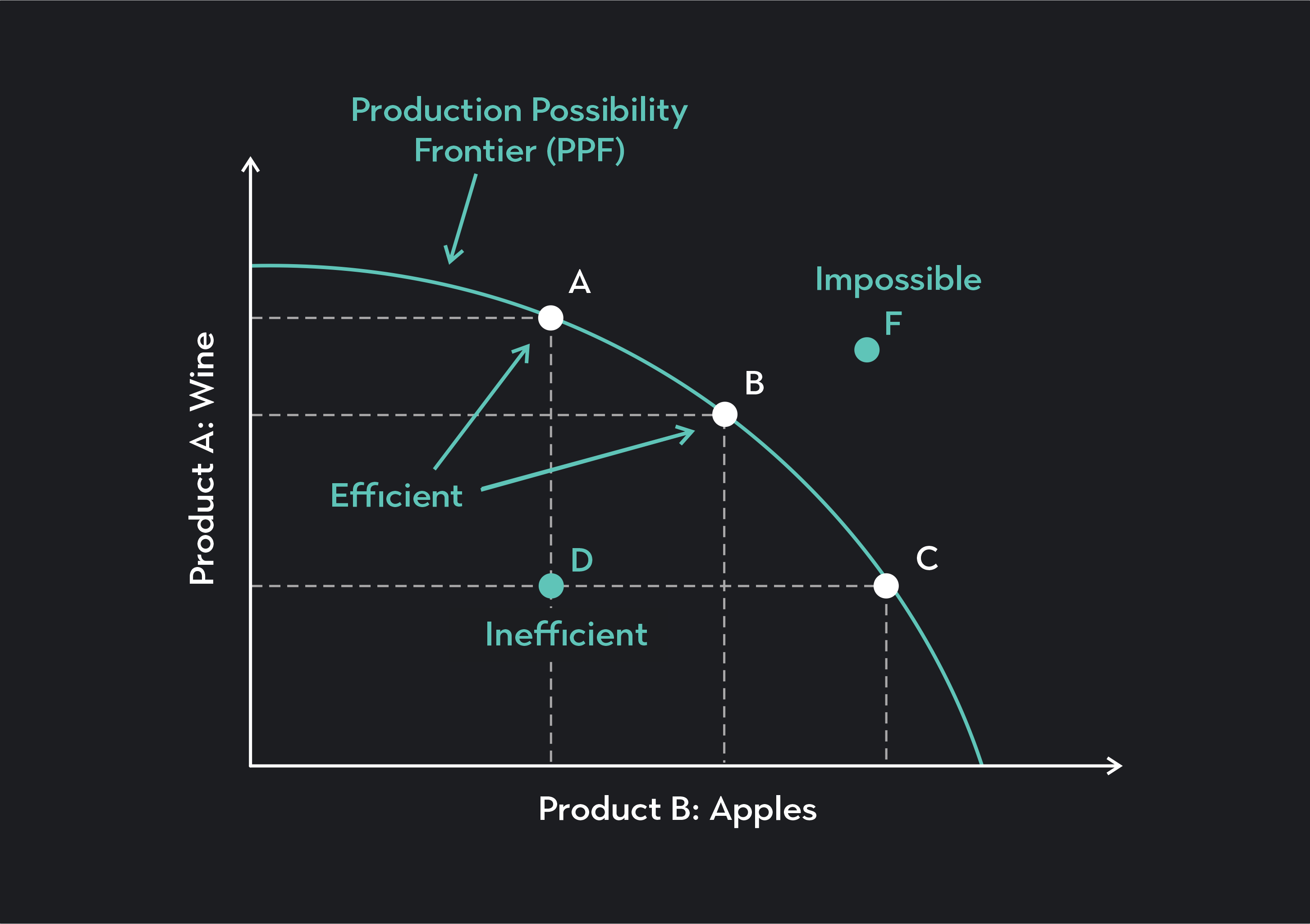
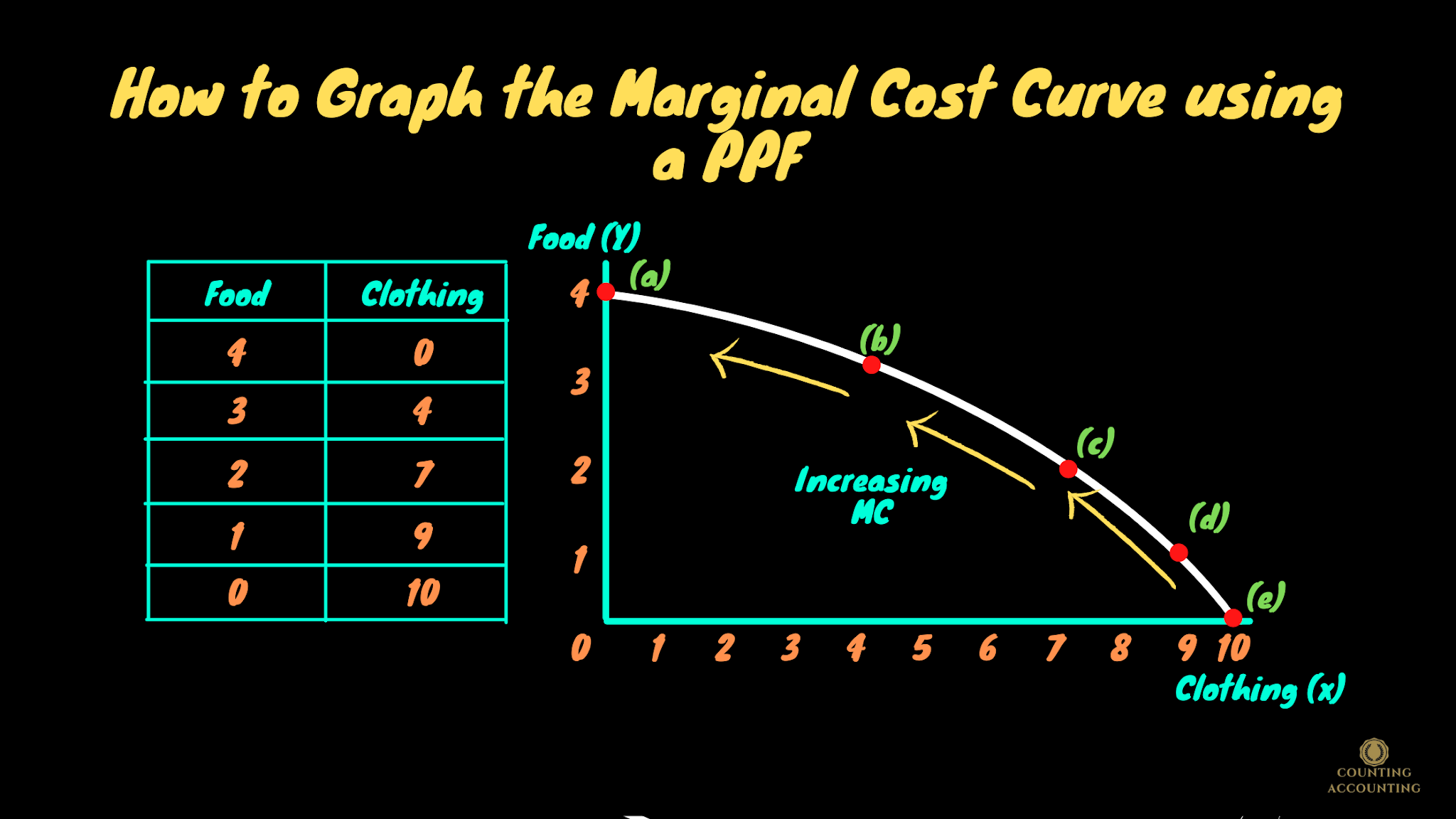
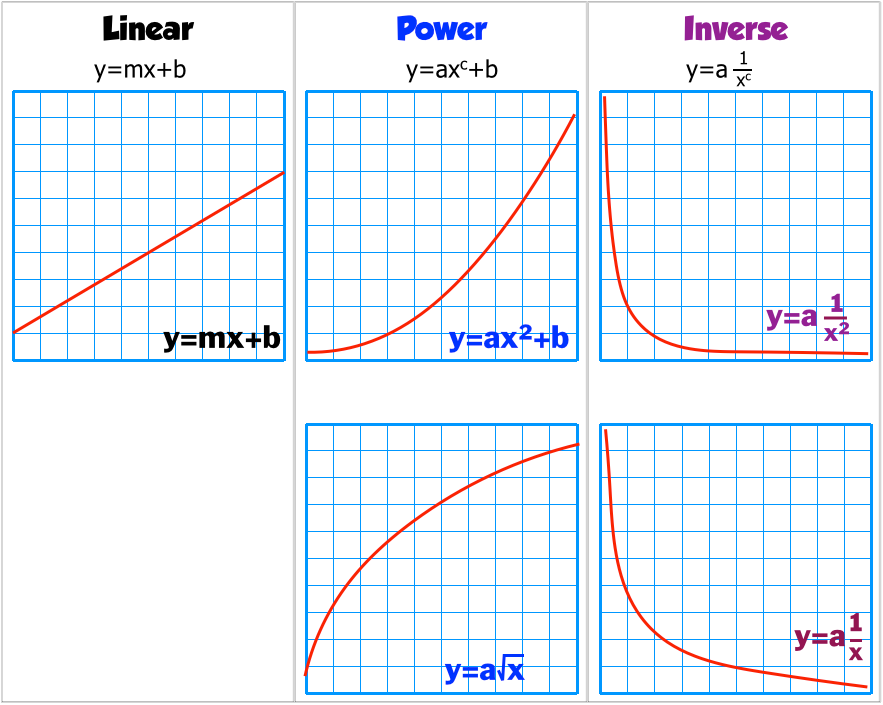
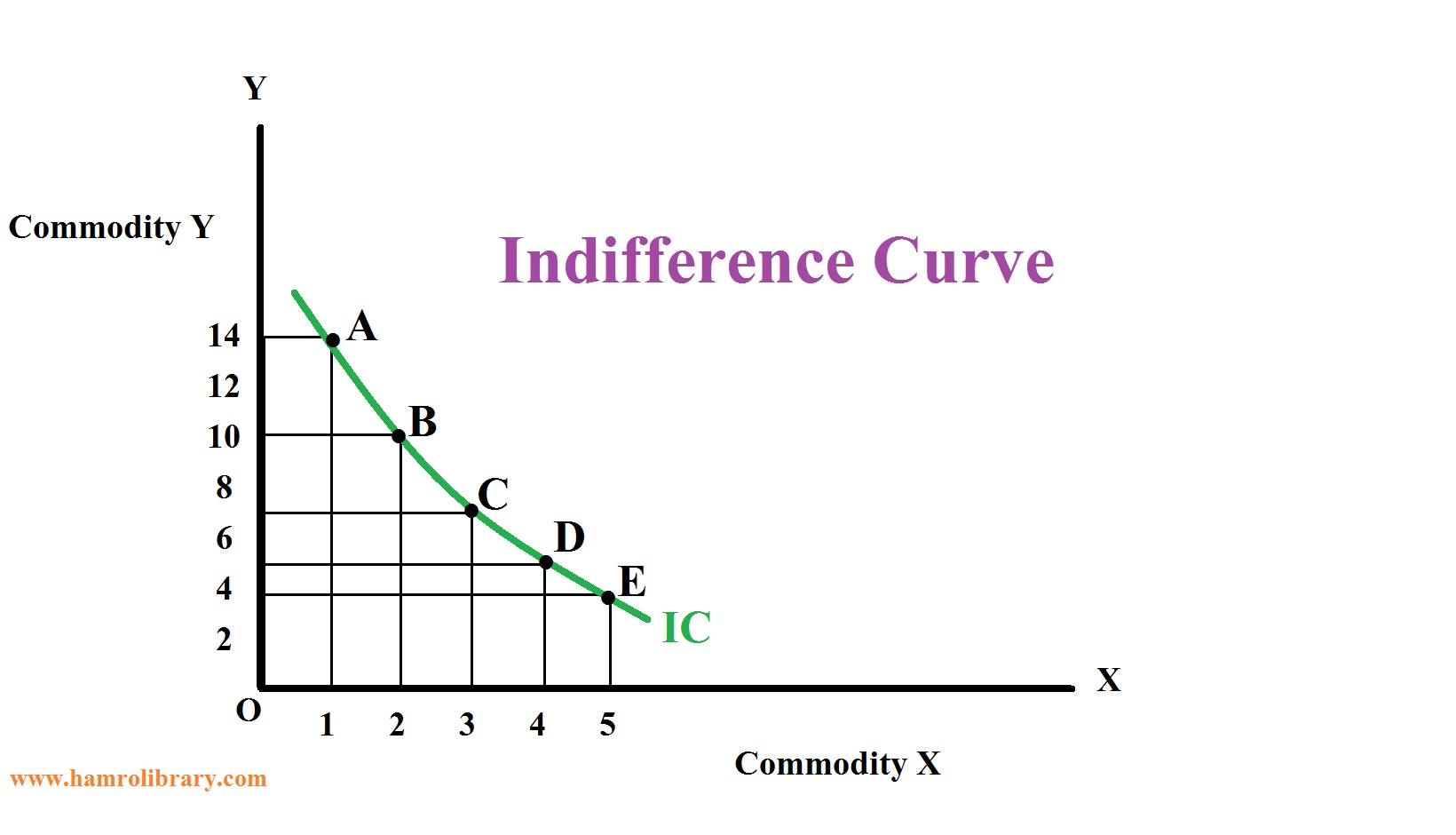
A curve is a continuous and smooth flowing line without any sharp turns and that bends. A curve showing all possible combinations that can be produced given the current stock of capital, labor, natural resources, and technology. The line of best fit could also be a curve.
Different types of graphs and charts are needed to present results from experiments. A curve is common in rates of reaction graphs. Diagram of perfect competition.
Understand how graphs show the relationship between two or more variables and explain how a graph elucidates the nature of the relationship. Apart from essential business presentation phrases, charts, graphs, and diagrams can also help you keep your listeners’ attention. Describing academic data with analysis and evaluation.
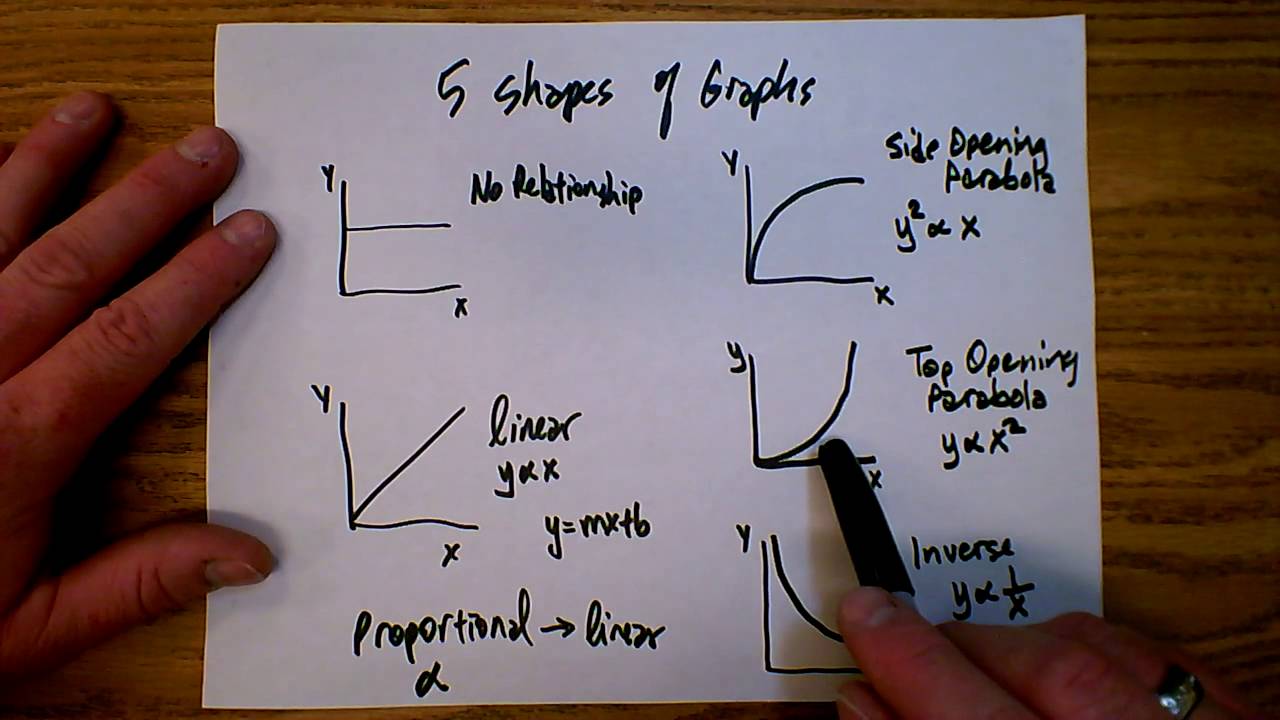
How to check data. A supply curve can often show if a commodity will experience a price increase or decrease based on demand, and vice versa. Transformation of functions means that the curve representing the graph either moves to left/right/up/down or it expands or compresses or it reflects.
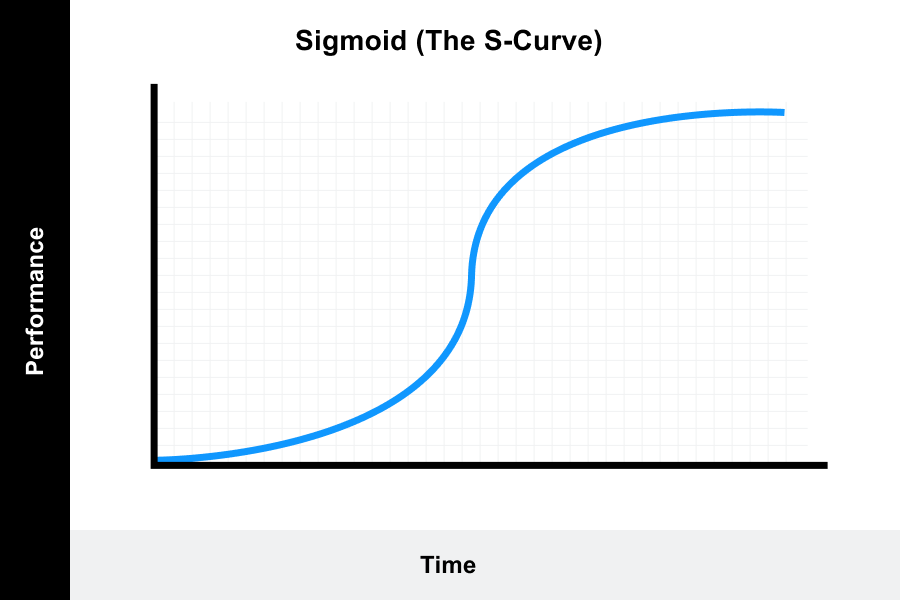
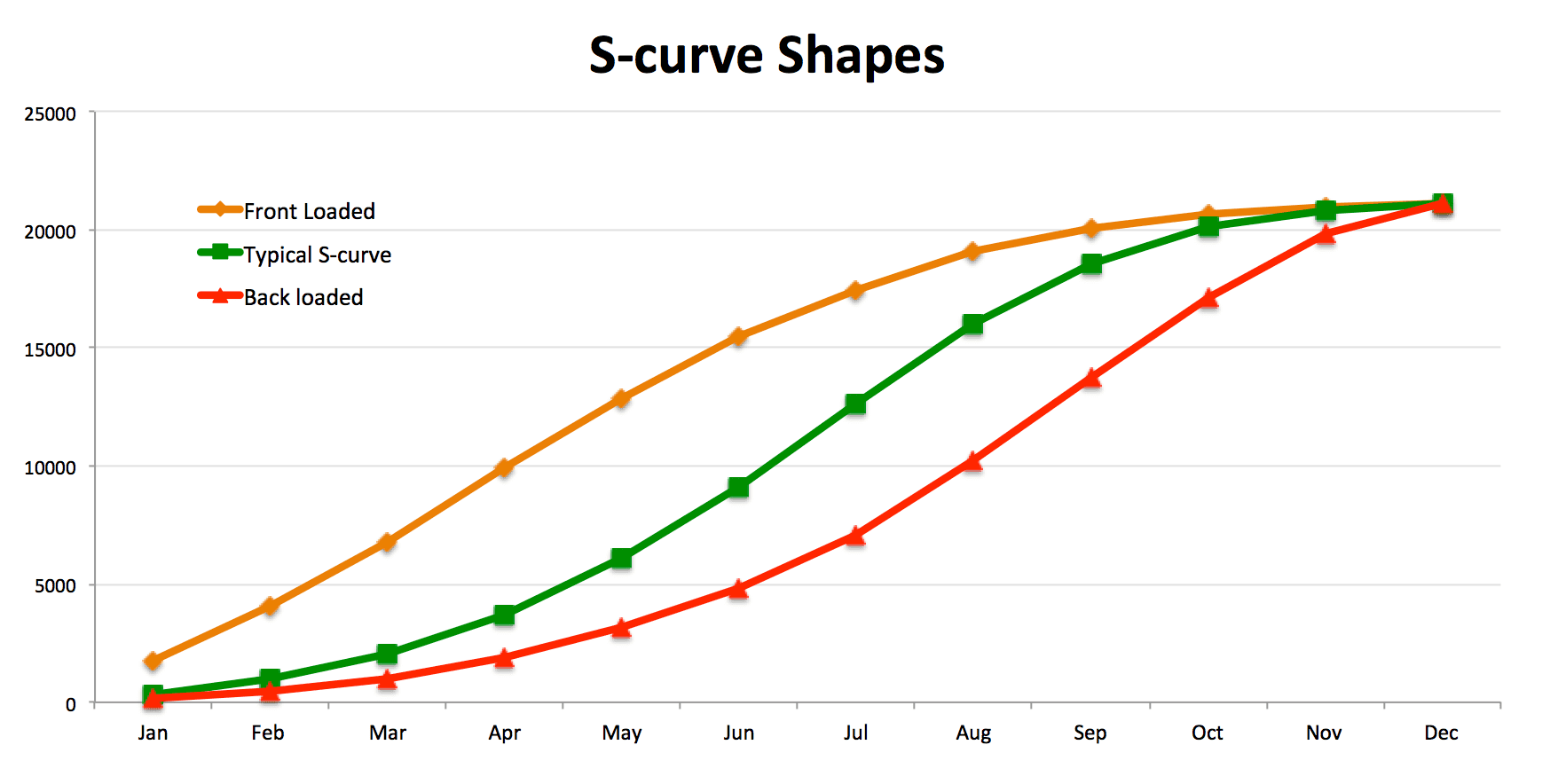
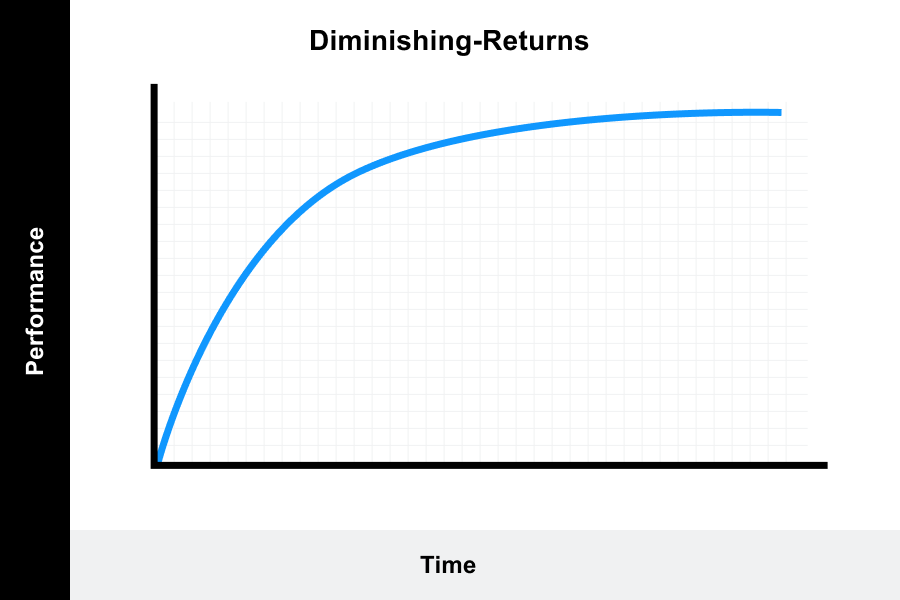
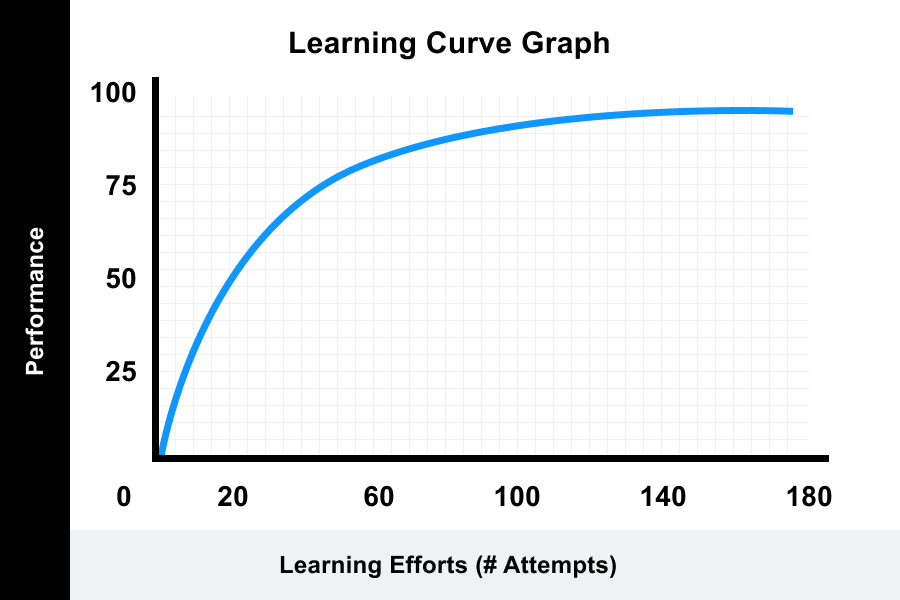
A learning curve is a correlation between a learner’s performance on a task and the number of attempts or time required to complete the task; In other words, curved lines are a form of a line that. How to describe academic graphs for presentations.
A straight line would indicate a constant rate of reaction, while a curve. A lot of presentations focus on data and numbers. Economies of scale and diseconomies.
The market price is set by the supply and demand of the industry (diagram on right) this sets the market equilibrium price of p1.