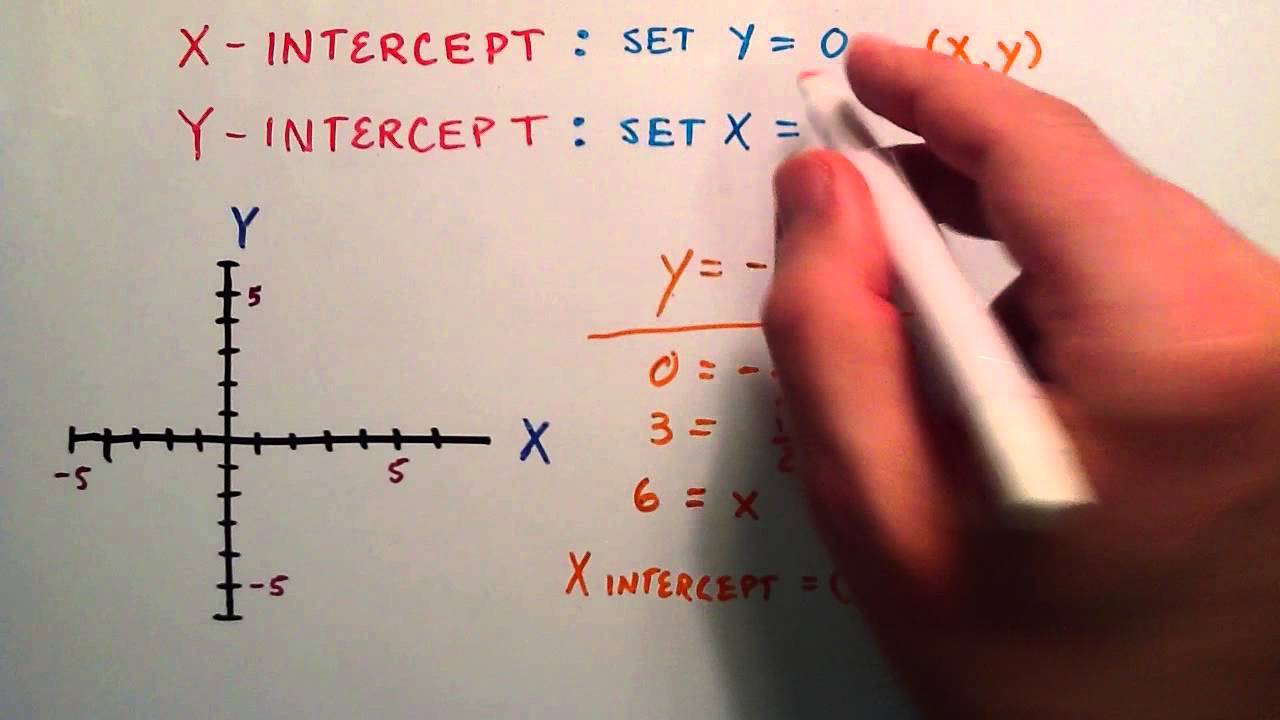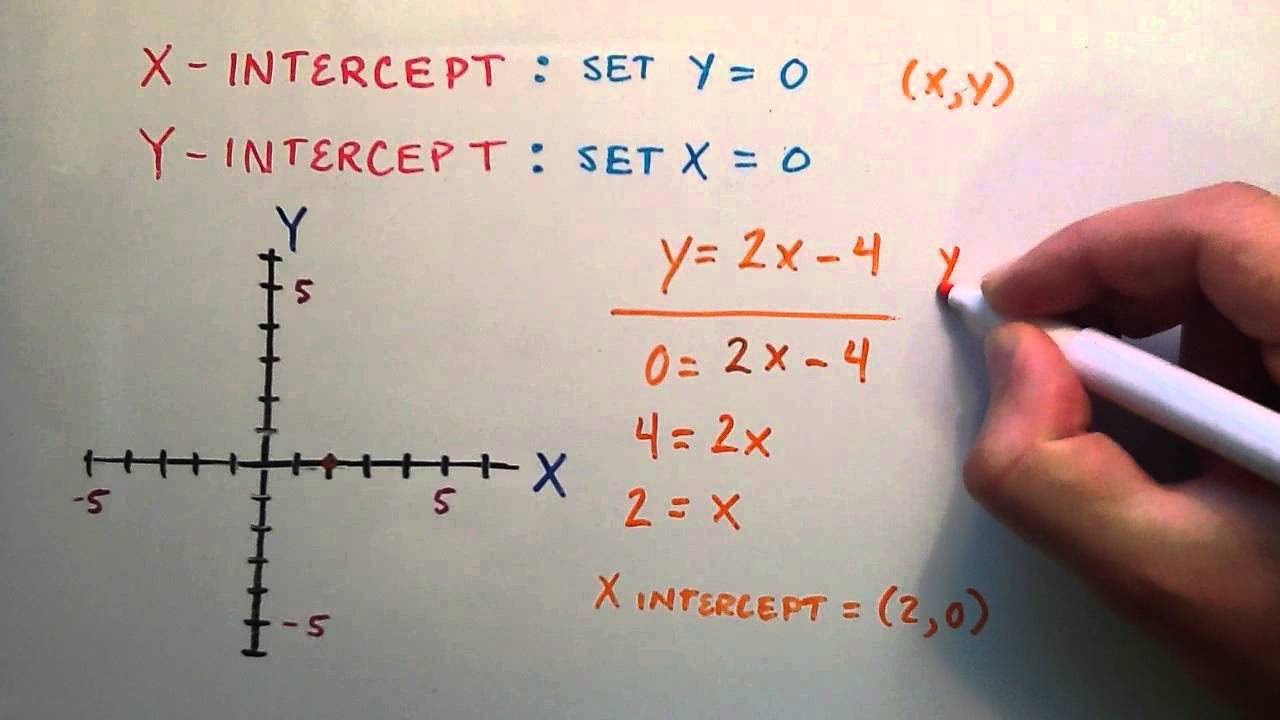Perfect Tips About How To Find Y-intercept With 2 Coordinates Tableau Dual Axis 3 Measures
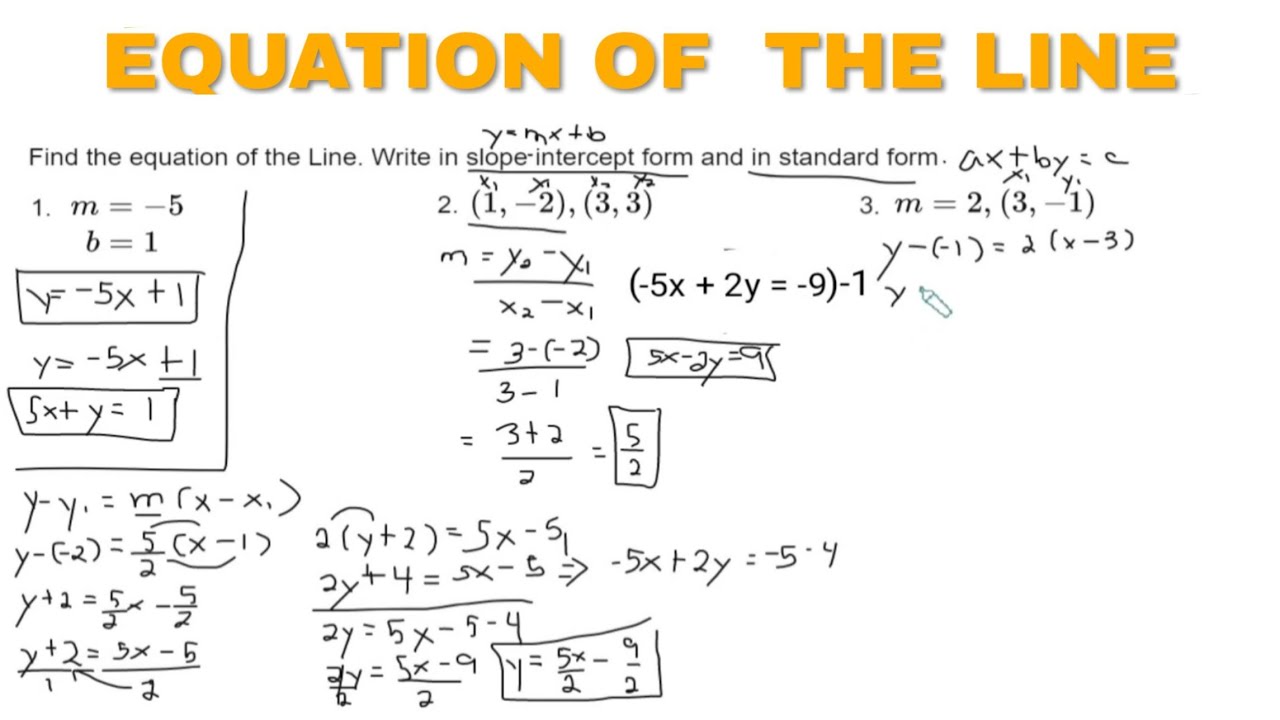
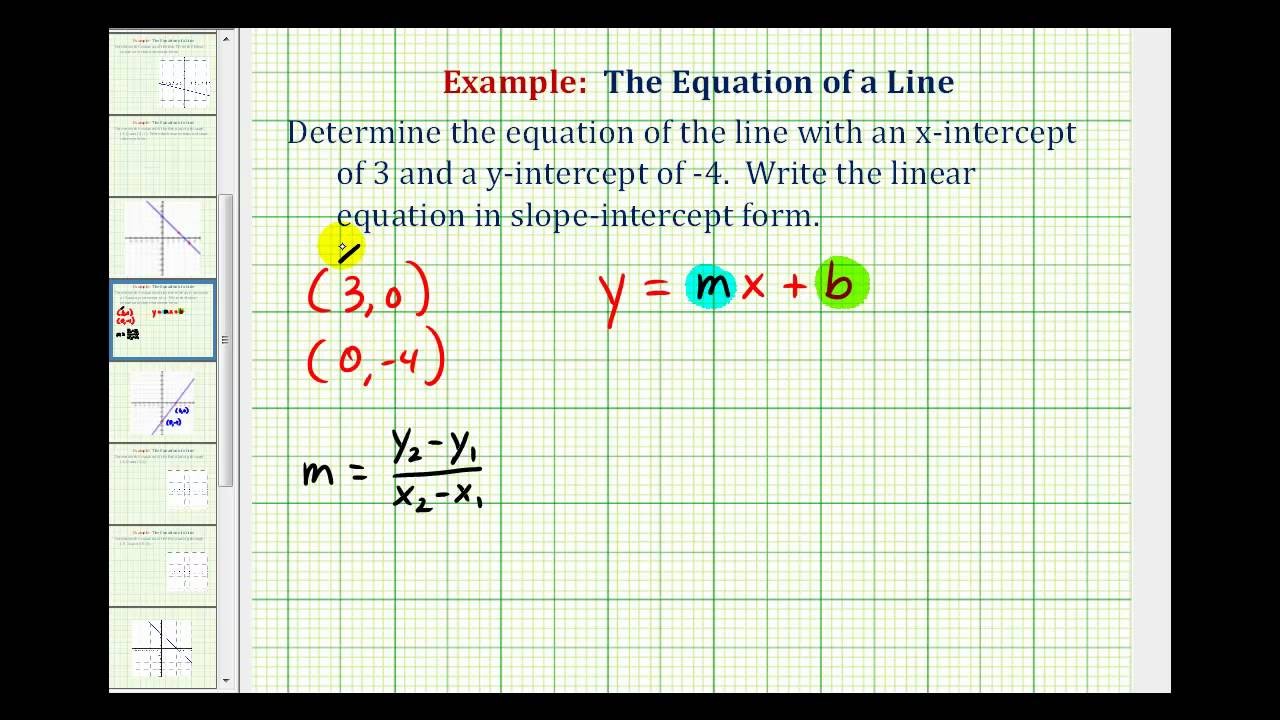
Given any two points on a line, we can algebraically calculate the slope using the slope formula, m = r i s e r u n = y 2 − y 1 x 2 − x 1.
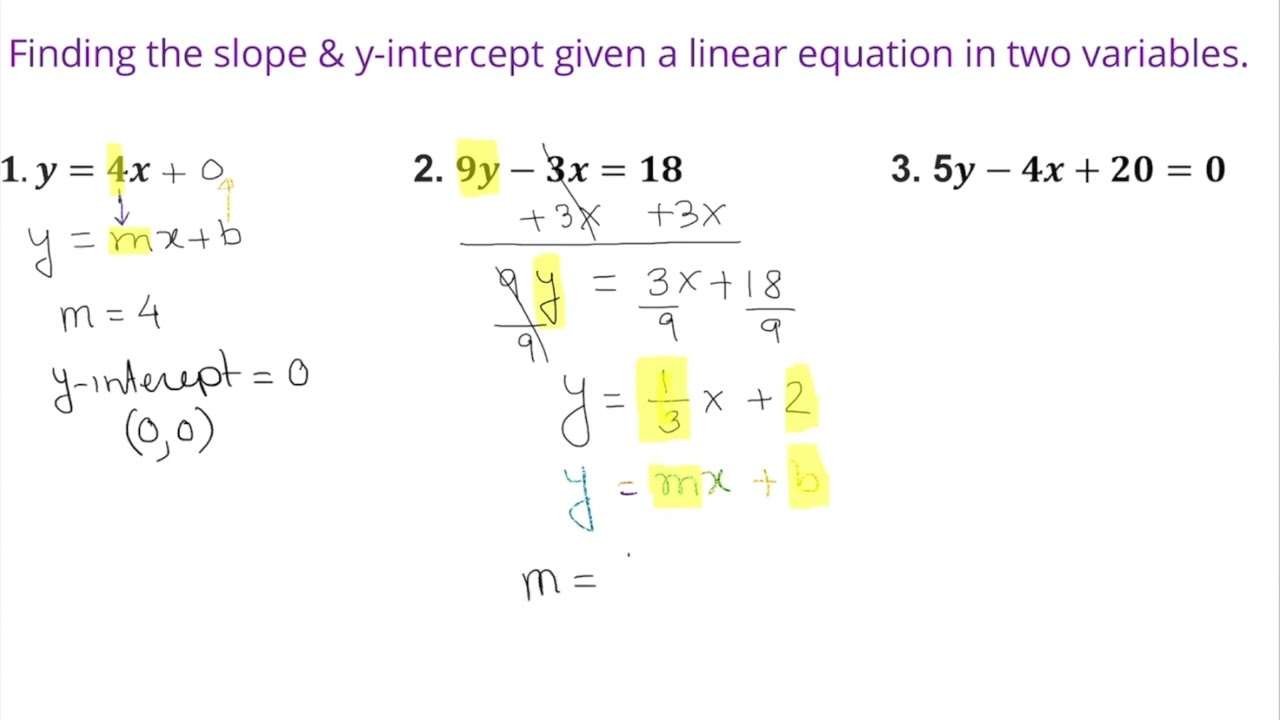
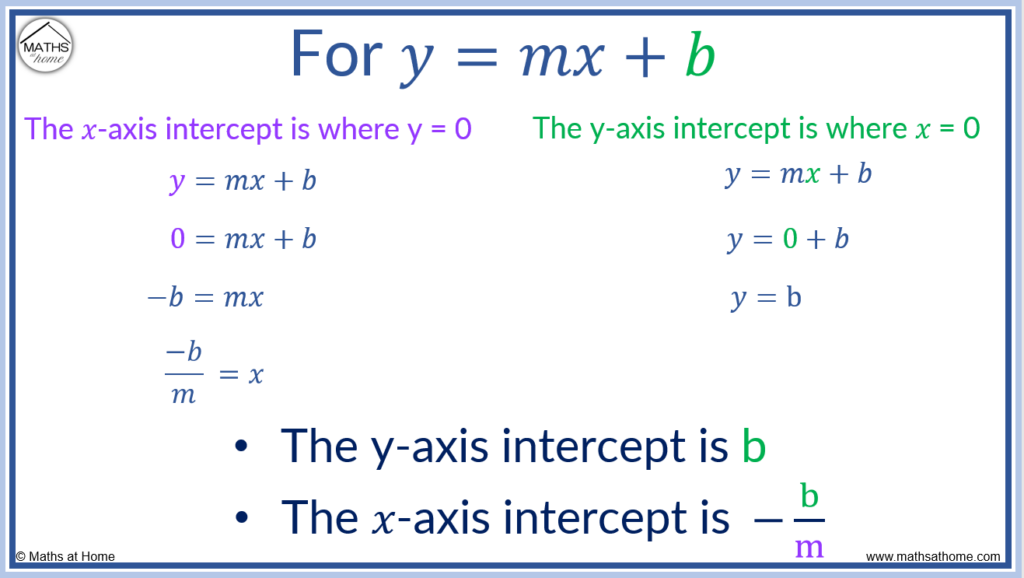
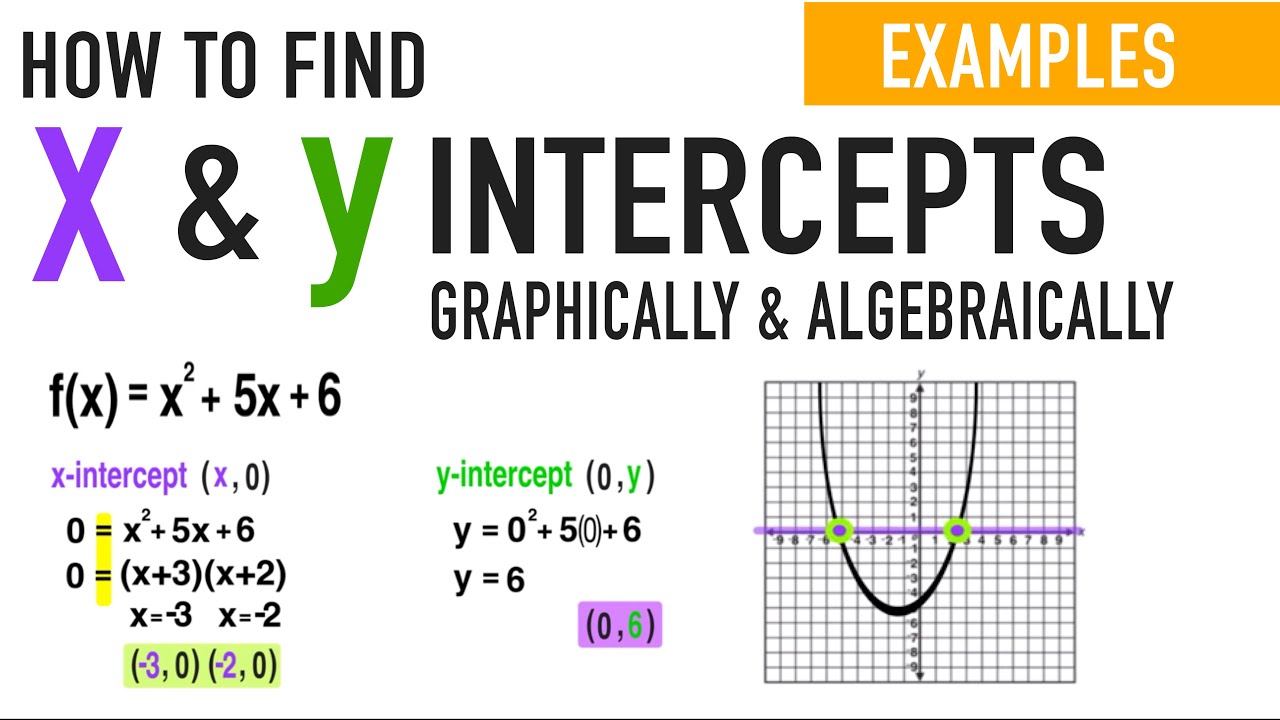
How to find y-intercept with 2 coordinates. Start practicing—and saving your progress—now: The equation of your function (same as the equation of the line). To find the y intercept using the equation of the line, plug in 0 for the x variable and solve for y.
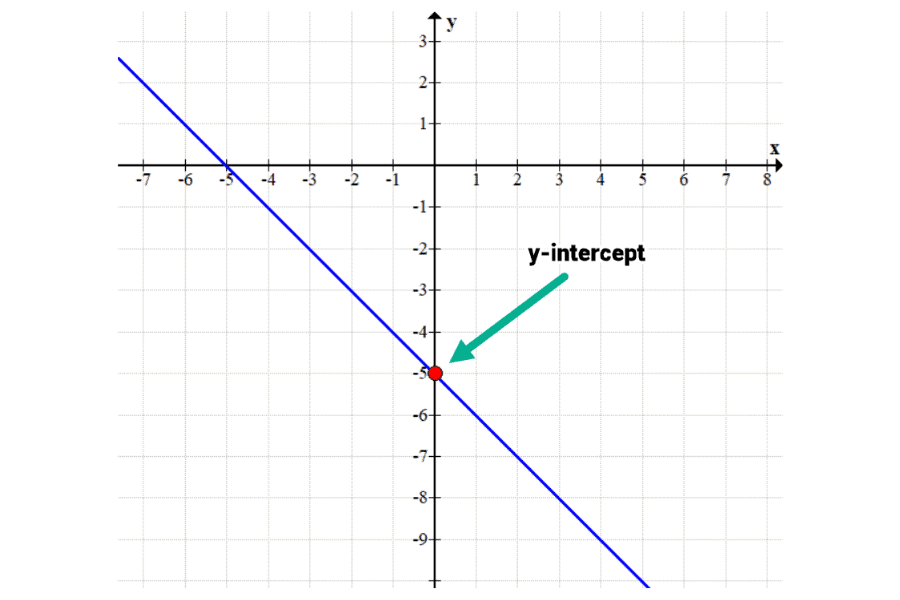
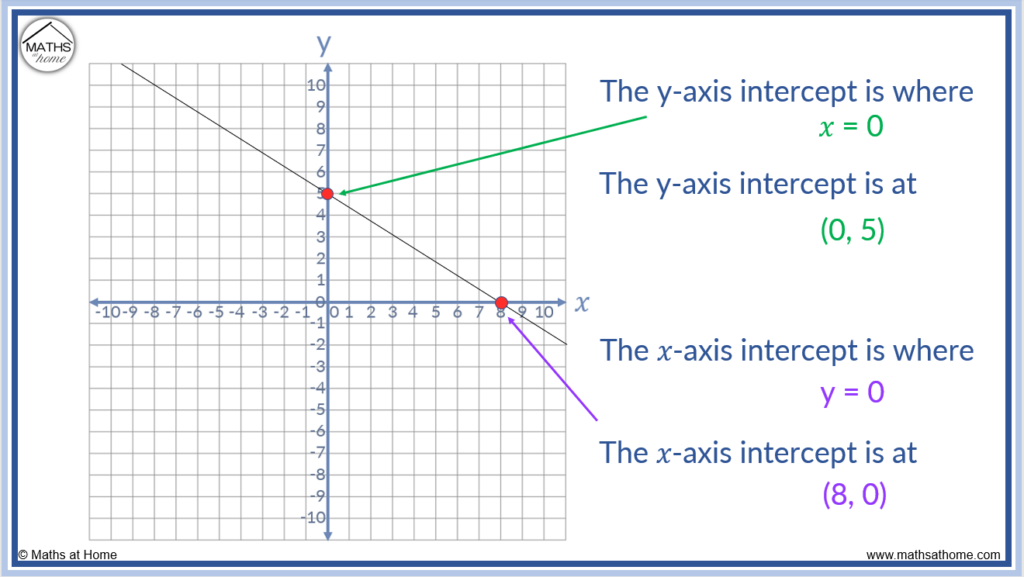
The points of the intecepts are (2,0) and (0,5). In the above diagram the line crosses the y axis at y = 1. The linear equation from two points (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) describes the unique line that passes through these points.
Q1 q2 q3 q4 q5 q6 q7 q8 q9 q10. Finding intercepts from an equation. What is the linear equation from two points?
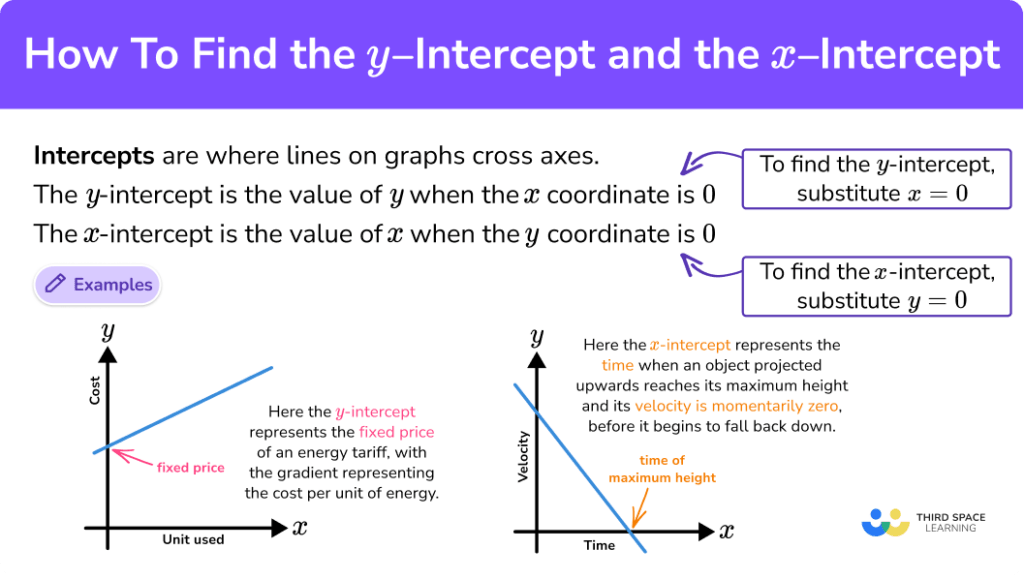
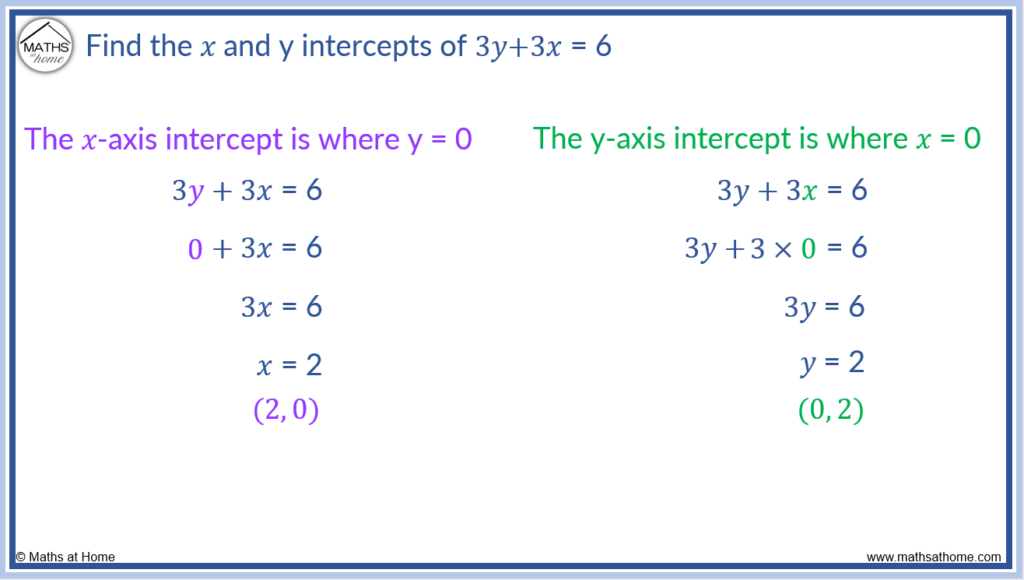
Here you will learn about how to find the y intercept from a straight line graph, including straight lines in the slope intercept form, y=mx+b and standard form, ax+by=c. Set y=0 then solve for x. We're asked to determine the intercepts of the graph described by the following linear equation:
When you want the x intercepts (x,0): This equation can be in the standard form ( ax + by + c = 0) or in. Since the table represents a line, there's a constant rate of change of y with respect to x.
3 x + 2 y = 5. X^{\circ} \pi \left(\square\right)^{'} \frac{d}{dx} \frac{\partial}{\partial x} \int \int_{\msquare}^{\msquare} \lim \sum \infty \theta (f\:\circ\:g) f(x) Here the line crosses the y axis at y = −2.
Enter the x and y coordinates of the second point on the line. 3 ⋅ 0 + 2 y = 5 2 y = 5 y = 5 2. Just find the value of y when x equals 0.
Courses on khan academy are always 100% free. When you want the y intercepts (0,y): Set x=0 then solve for y.
X^{\msquare} \log_{\msquare} \sqrt{\square} \nthroot[\msquare]{\square} \le \ge \frac{\msquare}{\msquare} \cdot \div: But the magic doesn't stop there, for you also get a bunch of extra results for good measure: Click the blue arrow to.
Verify your results using our y. Here, m = slope of the line. Standard form reads ax + by + c = 0, where a, b, c are integers.