Sensational Info About When Not To Use A Histogram Chartjs Axis Color

Difference between histogram and bar graph.
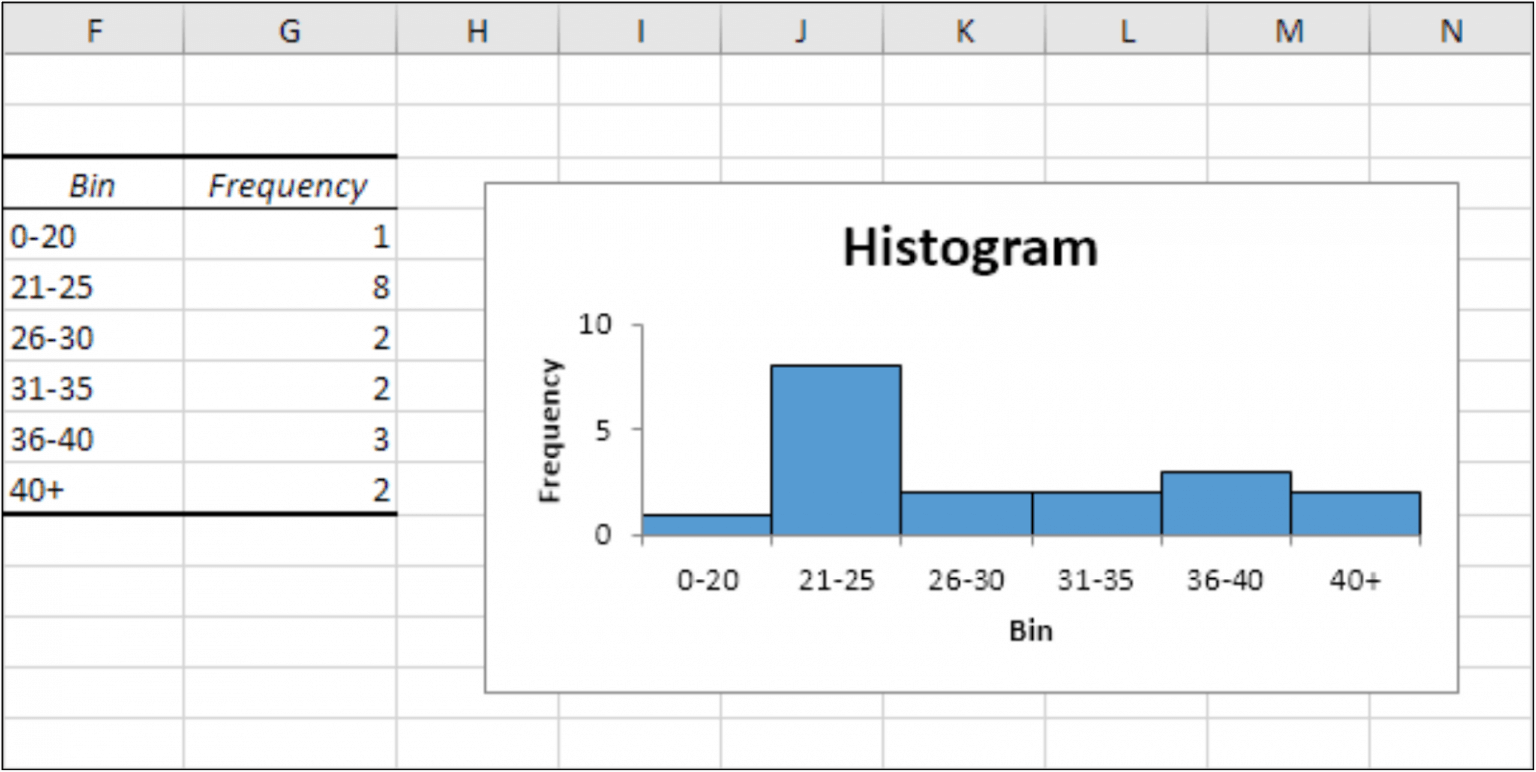
When not to use a histogram. This allows the inspection of the data for its underlying distribution (e.g., normal distribution), outliers, skewness, etc. Go to the insert tab, click on the insert statistic chart icon, and select histogram. It’s used in statistics to give a visual snapshot of the distribution of numerical data, revealing patterns such as skewness and central tendency.
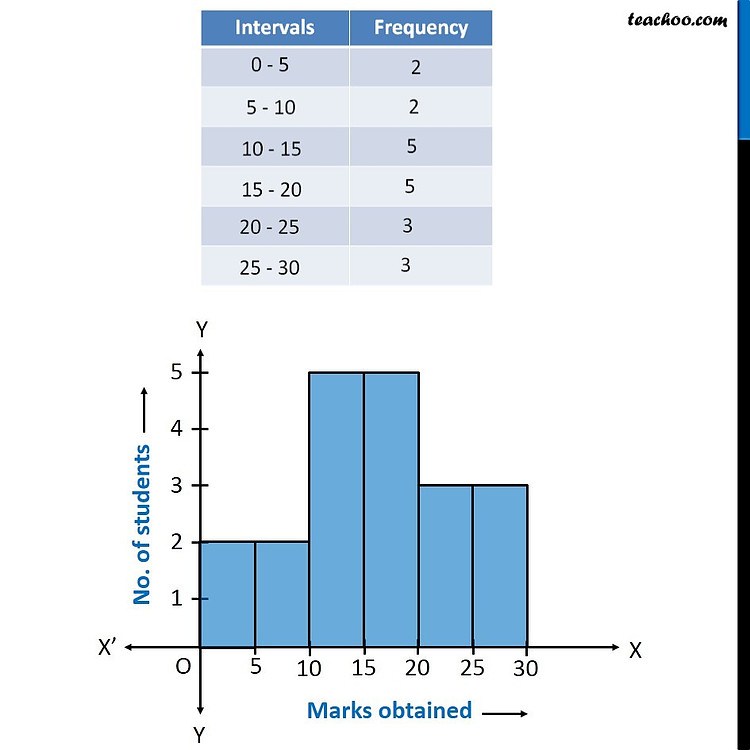
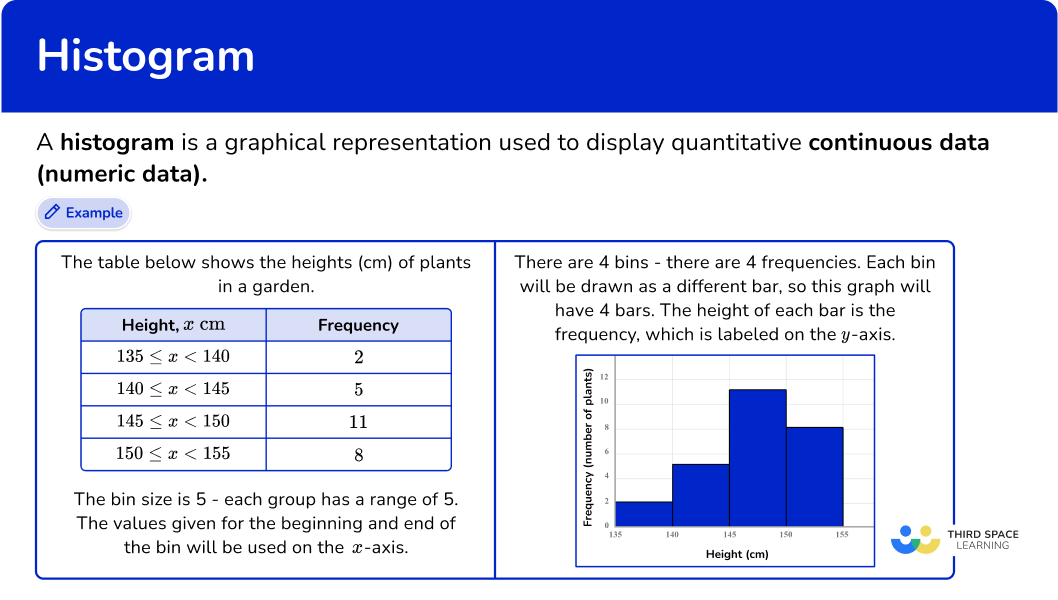
You measure the height of every tree in the orchard in centimeters (cm) The histogram refers to a graphical representation that shows data by way of bars to display the frequency of numerical data whereas the bar graph is a graphical representation of data that uses bars to compare different categories of data. It is similar to a bar chart, but a histogram groups numbers into ranges.
And you decide what ranges to use! A histogram is a graphical representation of data through bars, where each bar’s height indicates the frequency of data within a specific range, or bin. A histogram provides a visual representation of the distribution of a dataset:
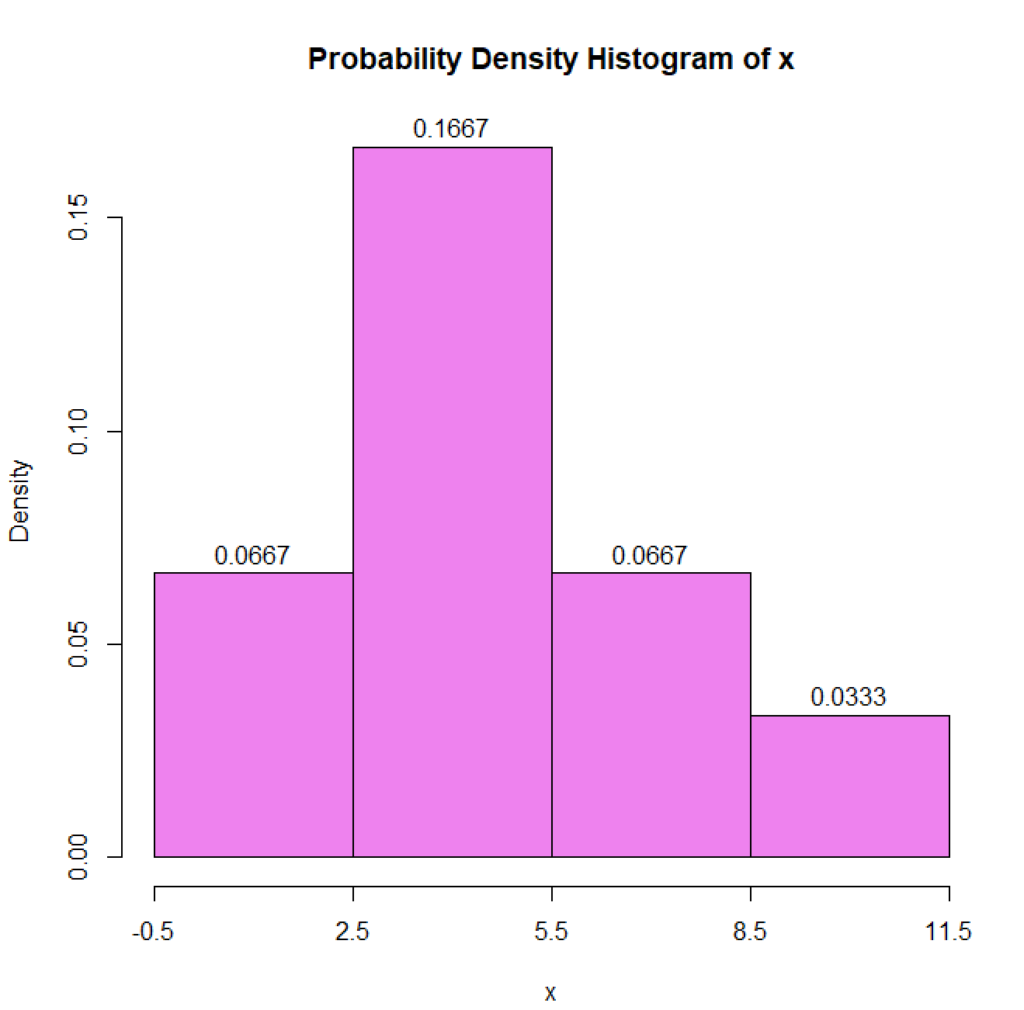
To do this, you need to use the number of observations and the range of values to decide a bin size and the number of bins needed to include all data points. It doesn’t allow to detect relevant values. Understanding their differences is important, so you know when to use each one and accurately convey—or consume—the insights they contain.
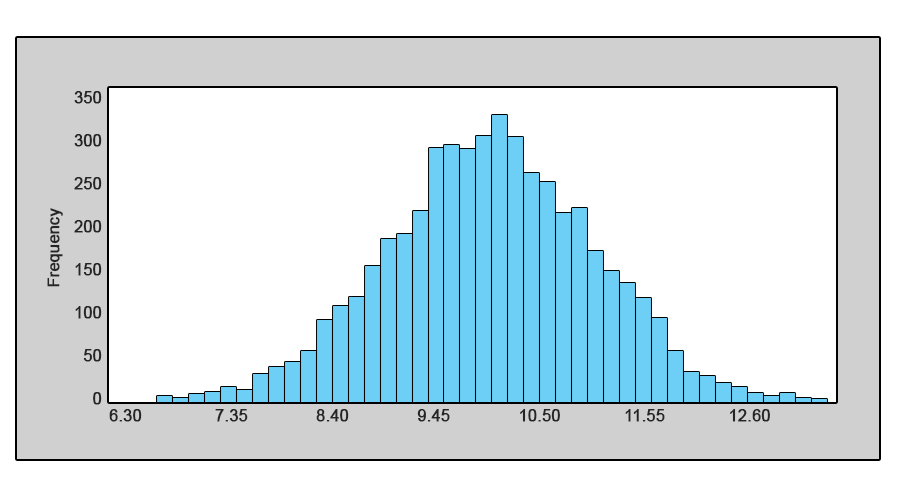
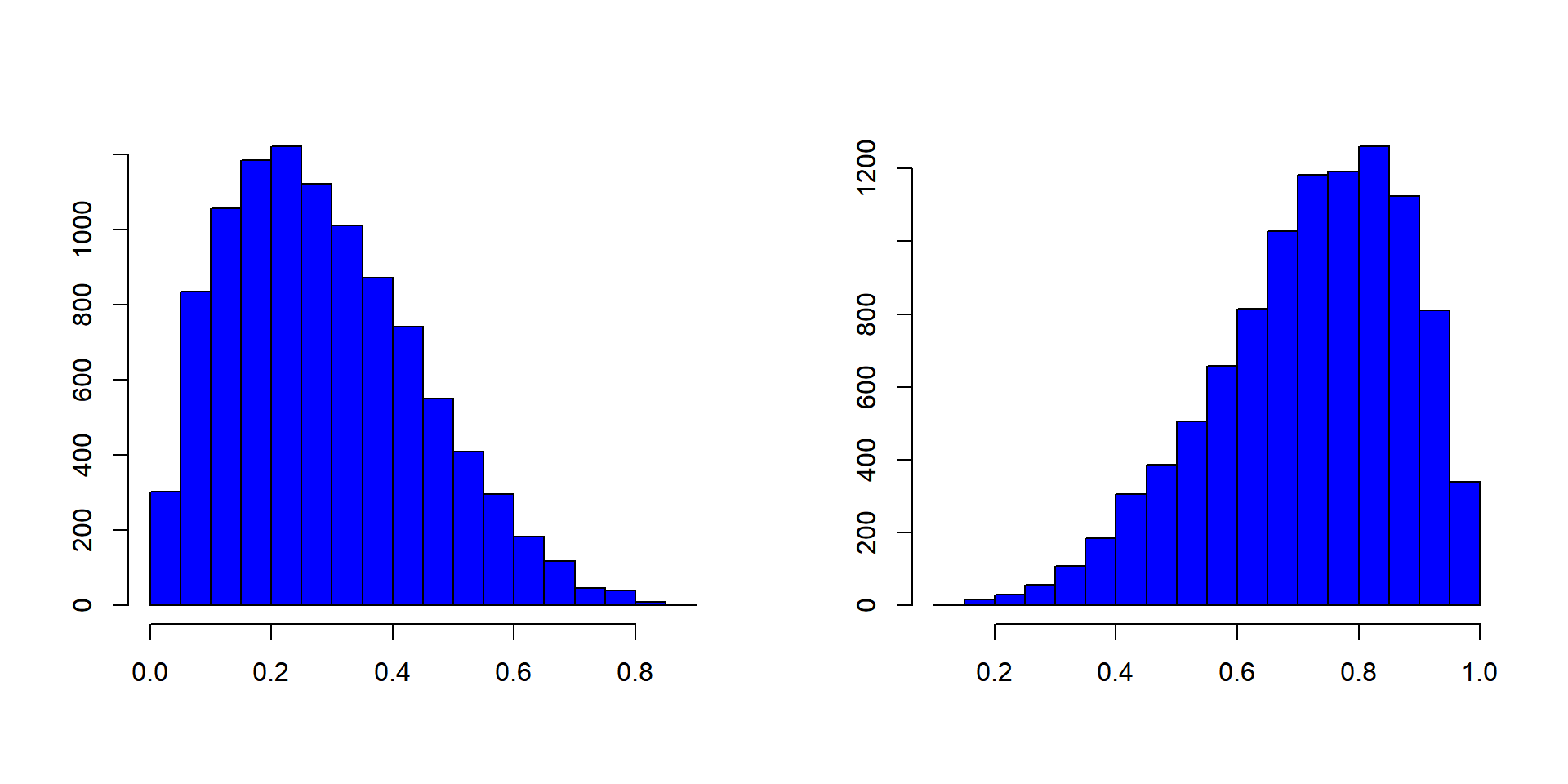
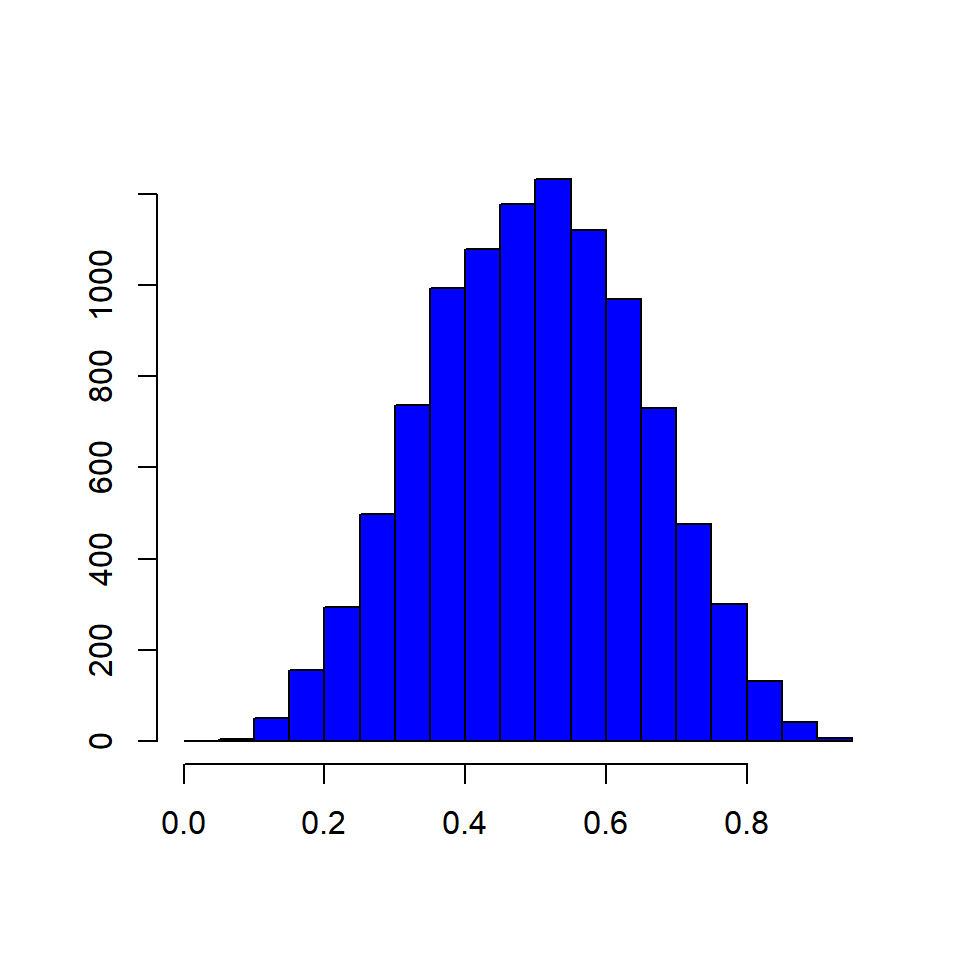
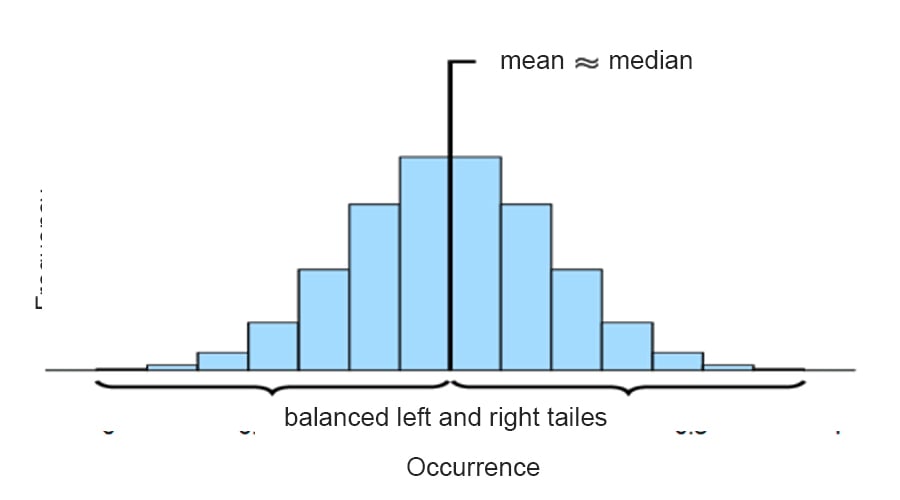
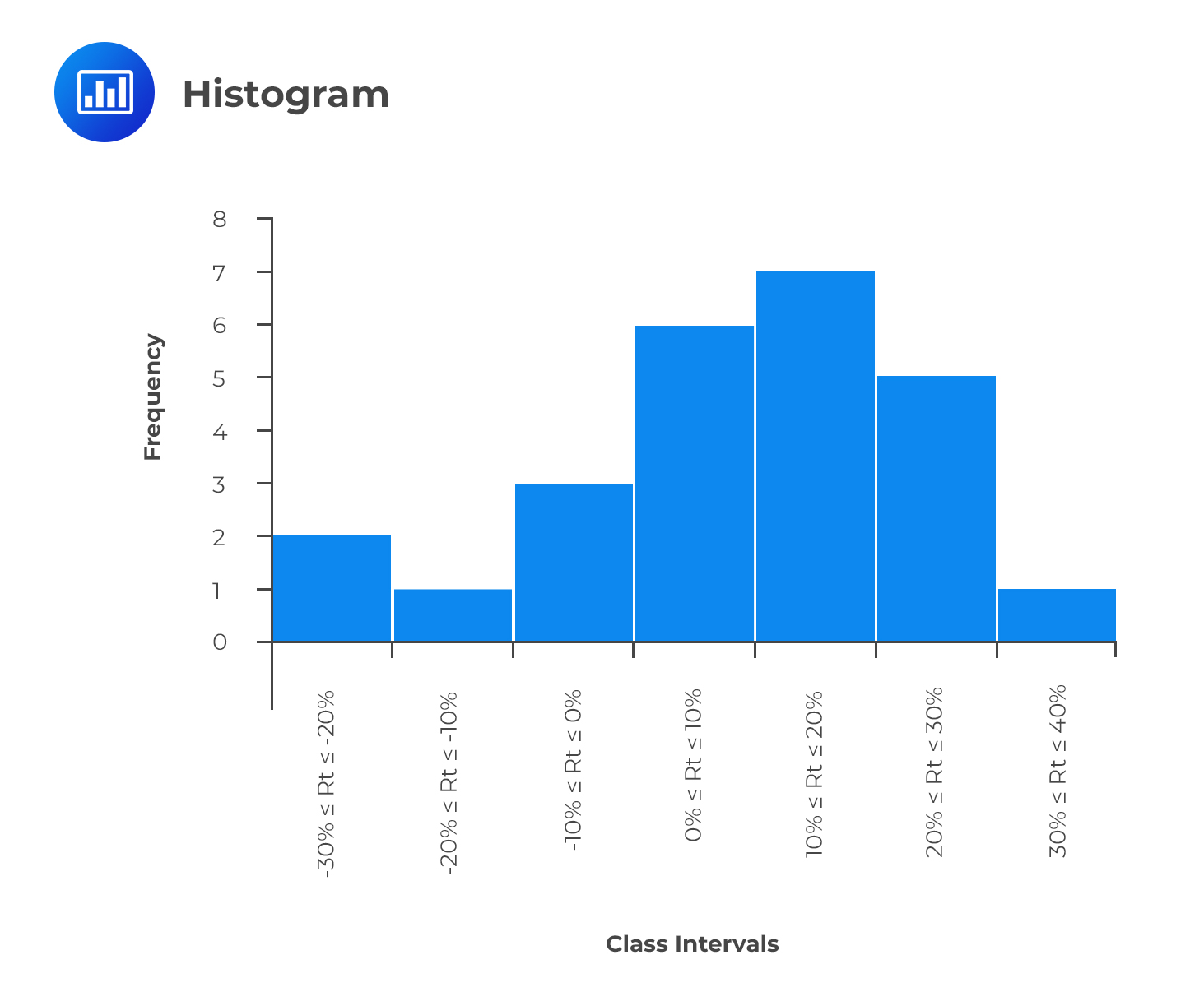
You can see roughly where the peaks of the distribution are, whether the distribution is skewed or symmetric, and if there are any outliers. It depends (too much) on the number of bins. You can also use them as a visual tool to check for normality.
A histogram is a graph that uses bars to show the distribution of a data set. Histograms help you see the center, spread and shape of a set of data. How to recognize, read, and understand a histogram.
Histograms provide a great way to evaluate data. A histogram is a visual representation of the distribution of quantitative data. Histograms are good for showing general distributional features of dataset variables.
The breakdown of salaries within an organization with the ability to see how balanced your pay scale is, or the count of bank members that have x amount of dollars in their accounts In addition, if it is unimodal, bimodal or multimodal. Let’s take a closer look.
Histograms are one of the seven basic tools in statistical quality control. A histogram is very similar to a bar chart. In this post, with the aid of some examples, we will go through 6 reasons why, when it comes to visualizing data, a histogram is hardly the best choice:
A histogram looks like a. Here's how we make a histogram: Taller bars show that more data falls in that range.






:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Histogram1-92513160f945482e95c1afc81cb5901e.png)